Embark on a journey into the fundamental building blocks of our universe with section 1 composition of matter answer key. This comprehensive guide delves into the nature of matter, its various states, and the properties that define its behavior.
From the smallest atoms to the vast expanse of galaxies, matter forms the very fabric of our existence. Understanding its composition is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of chemistry and the world around us.
1. Key Concepts: Section 1 Composition Of Matter Answer Key
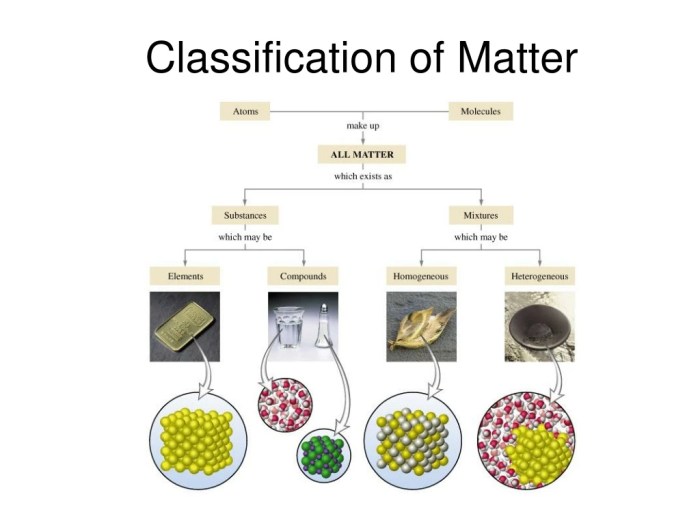
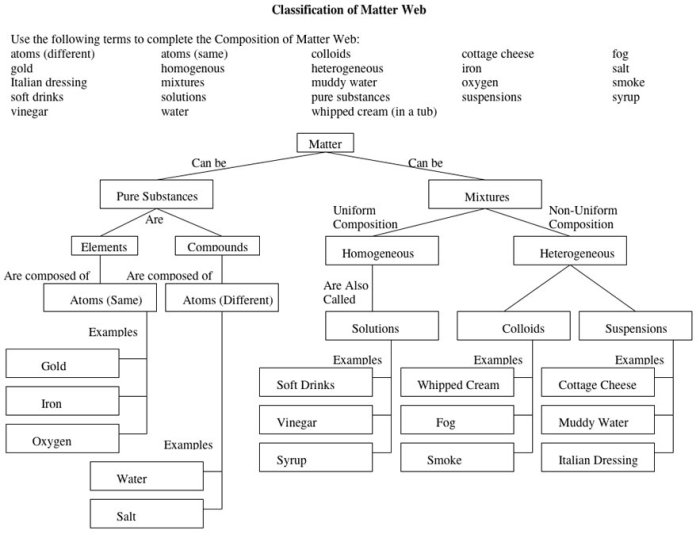
Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. It is composed of atoms, which are the smallest units of matter that retain the chemical properties of an element.
Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape, and gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
The properties of matter include density, hardness, malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
2. Chemical Elements and Compounds, Section 1 composition of matter answer key
| Element | Symbol |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen | H |
| Helium | He |
| Lithium | Li |
| Beryllium | Be |
| Boron | B |
Elements combine to form compounds through chemical reactions. Compounds have different properties than the elements that compose them.
Ionic compounds are formed when a metal loses electrons to a nonmetal. Covalent compounds are formed when two or more nonmetals share electrons.
3. Mixtures and Solutions
Mixtures are combinations of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. Solutions are mixtures in which one substance is dissolved in another.
There are different types of mixtures, including homogeneous mixtures (solutions) and heterogeneous mixtures (suspensions and colloids).
The properties of solutions include concentration, solubility, and boiling point.
4. Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are processes in which substances are transformed into new substances. Chemical reactions are represented by chemical equations.
The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
There are different types of chemical reactions, including synthesis reactions, decomposition reactions, single-replacement reactions, double-replacement reactions, and combustion reactions.
5. Energy and Matter
Energy and matter are related. Energy can be used to create matter, and matter can be used to create energy.
There are different forms of energy, including kinetic energy, potential energy, chemical energy, and nuclear energy.
Energy can be used to create and destroy matter. For example, nuclear reactions can create new elements and release energy.
6. Applications of Chemistry
Chemistry has many applications in everyday life. For example, chemistry is used to produce food, medicine, and clothing.
Chemistry is also important in various industries, such as the pharmaceutical industry, the chemical industry, and the food industry.
Chemistry plays a role in environmental protection. For example, chemistry is used to develop new technologies to clean up pollution.
Answers to Common Questions
What is matter composed of?
Matter is composed of atoms, which are the smallest units of matter that retain the properties of an element.
What are the different states of matter?
The three main states of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. Each state exhibits unique properties and behaviors.
What is the law of conservation of mass?
The law of conservation of mass states that the total mass of reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of products.