What ecosystem rivals the rainforest? This question has intrigued scientists and ecologists for decades. Rainforests are renowned for their unparalleled biodiversity, carbon sequestration capabilities, and complex food webs. However, other ecosystems around the world exhibit remarkable similarities to rainforests, rivaling their ecological significance and contributing to the planet’s environmental balance.
This exploration delves into the fascinating ecosystems that stand shoulder to shoulder with rainforests, showcasing their comparable biodiversity, carbon capture prowess, and intricate ecological dynamics. Prepare to be captivated as we uncover the hidden gems of the natural world that rival the grandeur of rainforests.
Ecosystems with High Biodiversity

Biodiversity, the variety of life on Earth, plays a crucial role in the functioning and stability of ecosystems. Rainforests are renowned for their exceptional biodiversity, but other ecosystems exhibit comparable richness in species.
Examples of Ecosystems with High Biodiversity
- Coral reefs:These marine ecosystems support an astonishing array of species, including fish, invertebrates, and algae.
- Estuaries:Where freshwater rivers meet saltwater oceans, estuaries create a unique and diverse habitat for a wide range of organisms.
- Grasslands:These vast, open ecosystems are home to a variety of plant and animal species, including grazing animals, predators, and decomposers.
Factors Contributing to High Biodiversity
Several factors contribute to the high biodiversity found in these ecosystems, including:
- Climate:Warm and humid climates provide optimal conditions for a wide range of species to thrive.
- Habitat heterogeneity:Diverse habitats within an ecosystem support a greater variety of species.
- Low disturbance:Ecosystems that experience minimal human disturbance tend to have higher biodiversity.
Ecosystems with Similar Carbon Sequestration

Rainforests play a vital role in sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Other ecosystems exhibit similar capabilities.
Ecosystems with High Carbon Sequestration Rates
- Oceans:The oceans absorb and store vast amounts of carbon dioxide through various mechanisms.
- Peatlands:These waterlogged ecosystems accumulate organic matter, effectively sequestering carbon.
- Temperate forests:These forests absorb and store significant amounts of carbon in their biomass and soils.
Mechanisms of Carbon Capture
The mechanisms involved in carbon capture in these ecosystems include:
- Photosynthesis:Plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis, converting it into biomass.
- Carbon burial:Organic matter accumulates in soils or sediments, preventing its release into the atmosphere.
- Chemical weathering:Rocks and minerals react with carbon dioxide to form stable compounds that lock away carbon.
Ecosystems with Complex Food Webs: What Ecosystem Rivals The Rainforest
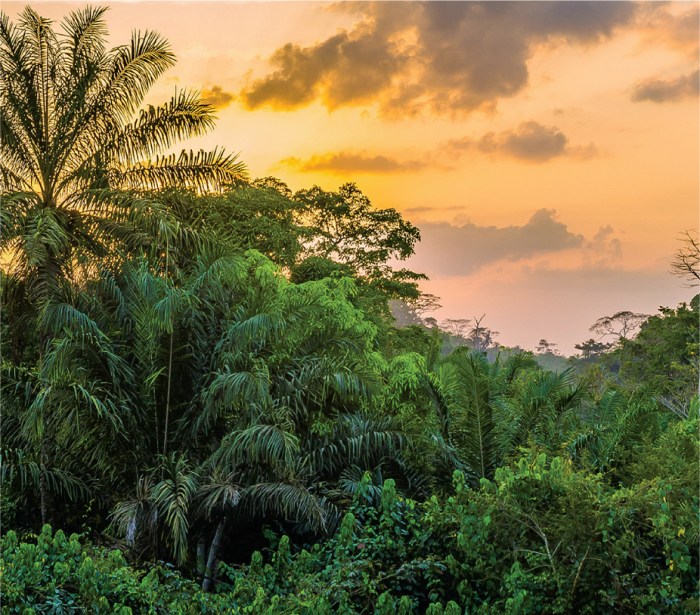

Rainforests exhibit intricate food webs, with multiple trophic levels and interconnected species. Other ecosystems also possess complex food web structures.
Ecosystems with Complex Food Webs
- Coral reefs:These ecosystems support a diverse food web involving algae, fish, invertebrates, and predators.
- Estuaries:Estuaries provide a rich food source for a variety of organisms, including fish, birds, and invertebrates.
- Savannas:These ecosystems support a complex food web involving grazing animals, predators, and decomposers.
Maintenance of Ecological Balance
The complexity of food webs in these ecosystems helps maintain ecological balance and stability by:
- Predator-prey relationships:Predators regulate the populations of their prey, preventing overpopulation.
- Nutrient cycling:Decomposers break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Symbiotic relationships:Species interact in mutually beneficial ways, supporting each other’s survival.
Ecosystems with Diverse Habitat Types
Rainforests encompass a wide range of habitat types, supporting a diverse array of species. Other ecosystems also offer similar habitat diversity.
Ecosystems with Diverse Habitats
- Coastal ecosystems:These ecosystems include beaches, salt marshes, and mangroves, providing habitats for a variety of marine and terrestrial species.
- Mountains:Mountains offer a range of habitats from lowland forests to alpine meadows, supporting a diverse array of species.
- Deserts:Despite their arid conditions, deserts support a variety of plant and animal species adapted to the extreme environment.
Support for Species and Ecological Processes
Habitat diversity in these ecosystems supports a wide range of species and ecological processes by:
- Providing niche specialization:Different species occupy specific habitats within the ecosystem, reducing competition.
- Maintaining genetic diversity:Diverse habitats promote the survival of different genetic variations within species.
- Facilitating ecosystem services:Habitat diversity supports essential ecosystem services such as water filtration and carbon sequestration.
Ecosystems with Unique Adaptations
Species in rainforests have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their complex environment. Other ecosystems also exhibit comparable adaptations.
Ecosystems with Unique Adaptations
- Desert plants:Desert plants have evolved water-conserving mechanisms such as thick cuticles and reduced leaf area.
- Arctic animals:Arctic animals have developed adaptations for survival in extreme cold, such as thick fur and blubber.
- Deep-sea organisms:Deep-sea organisms have adapted to high pressure and low light conditions, including bioluminescence and specialized sensory organs.
Evolutionary Pressures
The unique adaptations found in these ecosystems are driven by:
- Natural selection:Individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their genes.
- Genetic drift:Random changes in gene frequencies can lead to the accumulation of unique adaptations in isolated populations.
- Coevolution:Species interact and adapt to each other’s traits, driving the evolution of unique adaptations.
Ecosystems with Cultural and Economic Importance
Rainforests have immense cultural and economic value. Other ecosystems also hold similar significance.
Ecosystems with Cultural and Economic Importance, What ecosystem rivals the rainforest
- Wetlands:Wetlands provide important cultural and economic benefits, including flood control, water purification, and recreation.
- Mountains:Mountains offer cultural and economic value through tourism, agriculture, and mineral resources.
- Coastal ecosystems:Coastal ecosystems support fisheries, tourism, and cultural traditions associated with the sea.
Contributions to Human Well-being
These ecosystems contribute to human well-being by:
- Providing resources:Ecosystems provide essential resources such as food, water, and timber.
- Regulating ecosystem services:Ecosystems regulate climate, purify water, and control erosion.
- Supporting cultural and recreational activities:Ecosystems provide opportunities for cultural practices, tourism, and outdoor recreation.
Q&A
Which ecosystem rivals the rainforest in terms of biodiversity?
Temperate rainforests, savannas, and coral reefs exhibit comparable levels of biodiversity to rainforests.
What ecosystem sequesters carbon at a rate similar to rainforests?
Mangrove forests and peatlands play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, rivaling the efficiency of rainforests.
Which ecosystem boasts a food web complexity comparable to rainforests?
Coral reefs, with their intricate network of symbiotic relationships and trophic levels, showcase a food web complexity rivaling that of rainforests.
